
XIRR vs IRR
XIRR is used when the schedule of cash flows isn't periodic, whereas the IRR is used by analysts when the internal return rate is for a set of periodic cash flows.
The XIRR Function is classified as an Excel economic function. It is calculated by the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) for a collection of money flows that may no longer be periodic. It is done by assigning unique dates to every character's money flow.

The advantage of using excel's XIRR function is that you can accurately model these time-varying cash flows.
The function is an extended internal rate of return that considers cash flows, discount rates, and corresponding data to measure the return rate accurately.
In financial modeling, the characteristic is beneficial in finding out the cost of funding or perception of the feasibility of a challenge that does not typically have periodic money flows.
It helps us to identify or calculate the ROI price; therefore, it is often used to evaluate alternatives and decide between two or more additional investments.
Extended Internal Rate Of Return is an abbreviation of XIRR. It is a method of calculating the ROI of multiple trades made at different times. It is a good function for calculating returns when cash flows (investments or returns) are spread over time.
For mutual funds, whether you invest in a SIP or lump sum or repay with an SWP or lump sum, it handles all these situations and considers the timing of your investments and withdrawals to calculate your total return. It is used in cash flow investing activities.
How to calculate Xirr
It is the important one for calculating investments. It is the mathematical formula for calculating the annualized return on investments. Investment-related decisions are taken by calculating the Xirr, dates, amounts, and current or estimated values of investments.

Here,
- FV (Future value) is the cash flow at the end of the investment period.
- PV (Present value) is the initial investment.
- n is the number of periods over which the investment is made.
The syntax for the function is:

Where
- Values: It is the collection of values that corresponds to the sequence of cash flows (mandatory argument). It can reference a set of cells with values instead of an array.
- Dates (mandatory parameter): A date list matching the supplied values. Since the following dates are future dates of incoming payments or income and the first date is the start date, subsequent dates should be later than the first date.
- [guess] (viable argument): This initial guess or estimate of the IRR is just that-a guess or an estimate. Excel uses the default value of 10% if the value is absent.
Example: Assuming you invest £4,000, £9,000, £5,000, £4,000, and £6,500 SIP over 5 years and earn £53,000 after 5 years, your ROI is 22%.
The resulting value is called IRR. This concept determines how much money an investment will earn if its costs are evenly distributed over time.
However, assets are generally not evenly distributed with mutual funds. Mutual funds tend to invest and redeem at irregular intervals.
Compute the rate of return of any investments or policy like SIP or LIC.
We have invested the amount in policy instruments at irregular intervals on different dates. Now we want to know the return on the invested amount, so here we create a table and then solve the extended rate of return. Let's see
| Date | Policy Instruments |
|---|---|
| 1-01-09 | -10000 |
| 7-01-09 | -12000 |
| 1-01-10 | -10000 |
| 7-01-10 | -15000 |
| 1-01-11 | -13000 |
| 7-01-11 | -10000 |
| 1-01-12 | -10000 |
| 7-01-12 | -10000 |
| 1-01-16 | 120000 |
| 1-01-18 | 50000 |
Now, open an excel sheet to compute the XIRR. The steps are given below
- In column A, enter the dates of transactions.
- In column B, enter the policy amounts as a cash flow.
- Now type the formula of XIRR and select the policy instrument from B4 to B13; the dates are columns from A4 to A13.
- After the above steps, multiply it by 100 and get the returned output.
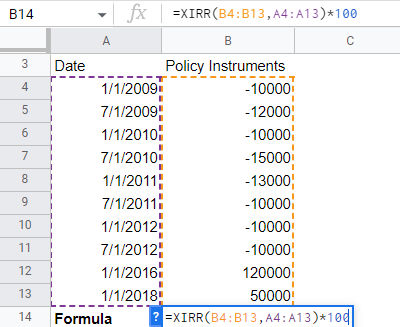
The resultant output is 10.90%.
Understanding IRR
IRR is used in financial analysis to estimate the profitability of a potential investment. In DCF modeling analysis, this discount rate sets the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows to zero.

Projected cash flows for a project or investment are provided in the IRR calculation and have a net present value of zero. IRR is the initial cash investment equal to the present value of future cash flows from the investment.
The internal rate of return is often compared to a company's critical rate or cost of equity. If the IRR is greater than or equal to the cost of capital, the company considers the project a worthwhile investment.
The value paid = present value of future cash flows; hence net present value = zero.
Once the internal rate of return is decided, it is usually compared to the company's critical rate or cost of equity.
Suppose the IRR is larger than or equal to the cost of capital. The company will accept the project as a possibility for investment, assuming that is the only basis for the decision.
Note
In practice, many other quantitative and qualitative factors are considered when making investment decisions.) An IRR lower than a critical ratio is rejected.
The "annual effective compound rate of return" (also known as the rate of return) sets the net present value of all of an investment's cash flows to zero, both positive and negative. It is a measure of the rate of internal return on investment.
In layman's language, it is the ratio at which the initial investment equals the net present value of future cash flows.
It is also the ratio at which the total present value of expenditure (cash outflow flows) equals the total present value of benefits (positive cash flows). It is used in capital budgeting in financial models.
How to calculate IRR
A popular scenario for the IRR in capital planning is to compare the profitability of starting a new business with the profitability of expanding an existing business. The internal rate of return is a given direction for evaluating whether a project or investment should proceed.
The IRR is also useful for companies evaluating stock buyback programs.
The manual formula for Irr is as follows

Here:
- R1 = Lower discount rate
- R2 = Higher discount rate
- NPV1 = Higher Net Present Value
- NPV2 = Lower Net Present Value
The syntax for the function is:

Where
- Values (mandatory parameter): This is an array of values representing the cash flow range. Cash flows include investments and net income. The value can reference a range of cells containing the value.
- [guess] (optional parameter): This is the user's guess for a number close to the expected IRR (since the IRR can have two solutions). The function will default to 0.1 (=10%) if omitted.
Example: Calculate IRR for monthly cash flow. Suppose you have been in business for ten months and now want to calculate the rate of return on cash flow. Finding IRR in Excel is very simple.
Enter your initial investment in a cell (B1 in this case). Since this is a payment, it must be negative.
Enter subsequent cash flows in the cells below or to the right of the initial investment (B1:B11 in this example). Because this money comes from sales, it is entered as a positive number.
We are now ready to calculate the project's IRR. = IRR(B1:B11,10%) The cash flows are given below for an initial investment.
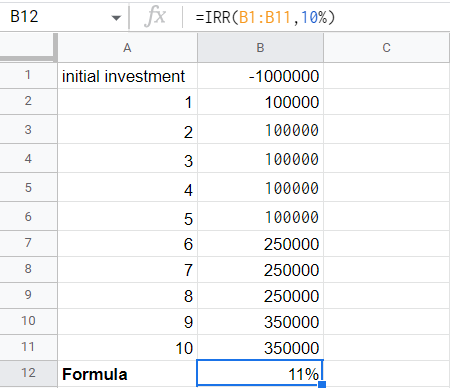
Using the IRR excel function, we get the internal rate of return is 11%.
Example: Here, we take another example of XIRR and IRR, both of the same amount. From this example, we can better understand the use of XIRR over IRR.
| Periods | Policy Amount |
|---|---|
| 1 | -100 |
| 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 20 |
| 4 | 30 |
| 5 | 40 |
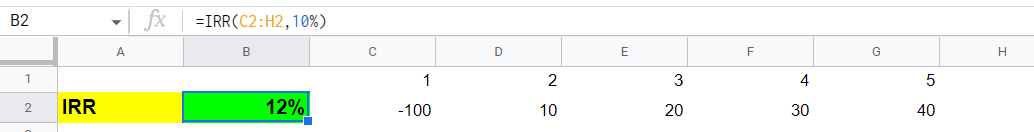
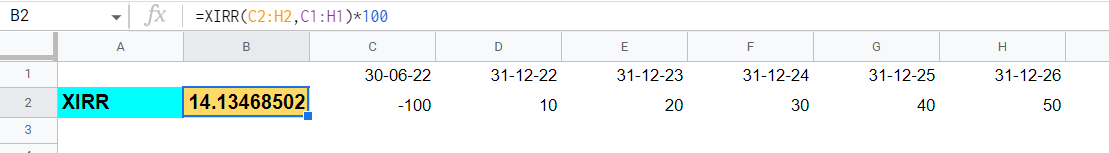
XIRR Vs. IRR Excel Financial Model
Understanding why we use XIRR versus IRR is critical through financial modeling and valuation. Using the simple IRR function in Excel can be misleading because it assumes that all periods of a cash flow series are equal.

So here is the distinction between Xirr and Irr to understand it concisely.
| Basis | XIRR | IRR |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | It is an approach to compute investment returns where numerous transactions happen irregularly. | It is a standard used in financial analysis to measure the profitability of future investments. |
| Syntax | =XIRR(values, dates,[guess]) | =IRR(values,[guess]) |
| Consideration | XIRR considers the best to evaluate the accurate results. | IRR considers the time value of money. |
| Time | It allows you to ascribe a date to each cash flow. So, use this function to calculate IRR for cash flows that are not necessarily periodic. | It assumes that all the periods in a series of cash flows are equal. You use this function to find the internal rate of return for periodic cash flows such as monthly, quarterly, or annual. |
| Assumptions | It assumes that daily compounding gives an effective annual rate return. | IRR function assumes a uniformly distributed annual cash flow. |

Everything You Need To Master Financial Statement Modeling
To Help You Thrive in the Most Prestigious Jobs on Wall Street.


or Want to Sign up with your social account?