
Current Assets
Assets that are expected to convert to cash within a year
The term assets means a resource that holds an economic value.The term current assets suggest any assets which can be sold or consumed through daily business operations. They include various resources which help a business function efficiently.

The formula is written as follows:
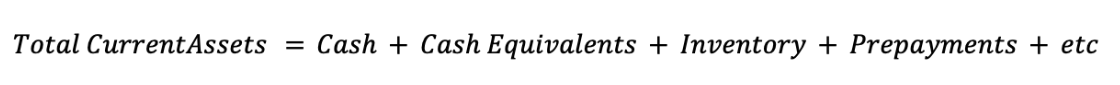
They include:
- Cash
- Cash Equivalents
- Cash/trade receivables
- Inventory
- Pre-payments
- Marketing securities
- Other liquid assets
The following are the main users of these assets:
- As a manager - The number of these assets maintained by a firm is critical for the company's management in terms of day-to-day business operations. Because money has a time value, accumulating too much can be detrimental.
On the other hand, a shortage can stymie corporate operations like any inventory item. In addition, bills and loans are due at the end of each month, and the company's management must be prepared to spend the cash to pay the debt.
Its monetary value shows the company's entire cash and liquidity situation. It also aids management in planning the essential arrangements for the smooth functioning of commercial operations.
- As a stakeholder - These are used to calculate accounting ratios such as current ratio, liquid ratio, working capital ratio, and so on for financial statement analysis.
Various stakeholders monitor such ratios and make judgments based on them. For example, liquidity ratios assess a debtor's ability to repay the debt. The dividend payout ratio assists investors in determining the company's dividend payments.
Where can you find Them?
A balance sheet or statement of financial position is a document provided to the company's stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, etc., that shows the company's financial position. This includes critical information about the company, such as - assets, liabilities, equity, etc.
The formula for the balance sheet is as follows:
Shareholder's Equity =Assets-Liabilities
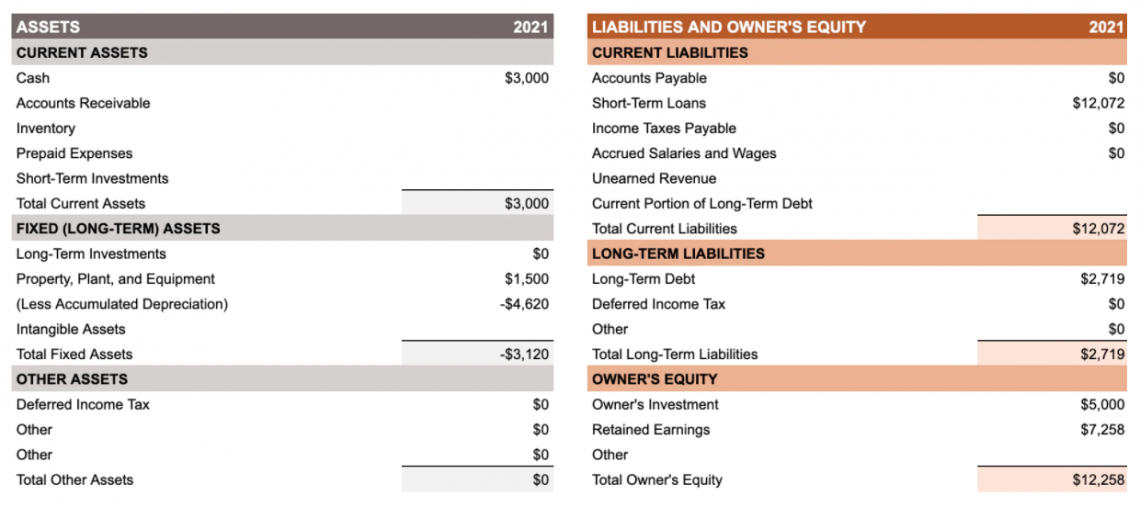
Financial statements of a company, such as - a balance sheet, income statement, etc., can be used to assess the liquidity and efficiency of a business and the rate of return it is providing to its shareholders. For example, the Current Assets are shown under the assets column on the balance sheet. Let us see an example of the same:
The above example clearly shows that there are broadly two kinds of assets: current and non-current assets (long-term assets). However, this article will limit our discussion to current assets.
Microsoft Excel is one of the most used applications to prepare financial statements for a company. This is because it offers various features to assist users in creating or editing financial data.
Sign Up for our Free Excel Modeling Crash Course
Begin your journey into Excel modeling with our free Excel Modeling Crash Course.
Ratio Analysis
Ratio Analysis is really helpful for a business to ascertain important information about the company, such as its - operating efficiency, profitability, liquidity, etc. It also helps businesses compare themselves to their competitors and take remedial action to improve their overall efficiency.

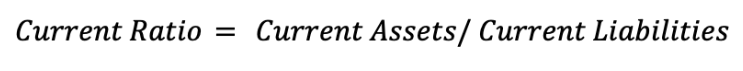
The current ratio is a liquidity ratio. It measures a company's capacity to pay off all its current liabilities. Current liabilities are defined as those which have to be paid within one financial year.
An excellent current ratio determines the liquidity position and financial health of a business. For example, a current ratio of 1.5-3 is usually considered a good ratio. However, these also depend on the company's nature or the industry the company is operating.
Efficient ratio analysis can help highlight the problems and other issues in the business. However, such ratios usually help only in identifying the problem, and the management of the company still has to decide the remedial action.
Similar to the Current Ratio, another Ratio known as the Acid Test Ratio (Quick Ratio) helps to determine the liquidity of assets in a business. The formula for acid test ratio are listed below.

This ratio can also be determined from the information provided on the balance sheet. A normal Acid test ratio for a business should be 1:1 or higher. Overall, The higher the acid test ratio is, the better the liquidity of a business.
Another ratio that helps stakeholders analyze the overall liquidity of a business is the cash ratio. It is the most commonly used method to determine a business's liquidity. For example, if a company is to pay off all its current liabilities, this metric shows its ability to do so without liquidating or selling other assets.
The formula for cash ratio is:

There is no ideal figure for a normal or good cash ratio. However, a cash ratio of 0.5-1 is usually considered ideal. But, again, ratios greatly depend upon the nature of the business and must not be analyzed in isolation.
For example, for a company having £200,000 and £150,000 in short-term liabilities, the company's cash ratio is 1.33, which is considered a good cash ratio.
Current Assets Vs Fixed Assets
They can be compared based on their liquidity and holding period.

The fixed assets are recorded on the net asset value is depreciation subtracted from the asset value. At the same time, the current asset is recorded at the cost or market value.
| Basis | Current Assets | Fixed Assets |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Also known as short term assets. | Also known as non-current or long term assets. |
Term Period | Generally consumed in less than a year | Possess an economic life of more than a year |
Depreciation | They are not subjected to depreciation as they are released in a short period of time. | They are subject to depreciation as the company owns them for a long time. |
Function | Used for daily funding & business operations | Used to generate mainstream revenue for the company.. |
Examples | Inventory, cash, cash equivalents, cash receivables, short term investments, prepaid expenses. | Plant & equipment (P&E), physical assets, vehicles & machinery, furniture, buildings etc. |
Examples of Current Assets
- Cash - The first line item on an organization's balance sheet increases the debt and decreases the credit. It is positioned at the top of the current asset section as items are arranged in order of their liquidity. It is one of the most liquid assets used to purchase other assets easily.

Cash assets include treasury bills, market funds, commercial papers, and other assets which can be easily converted into cash. Another kind of asset is cash value assets. These consist of both market value and cash value.
- Commodities - Commodities or goods are the most volatile assets present. They are considered "Real Assets," thus reacting to the constantly changing economic world. Commodities possess both high risk and high volatility but can act as a counterweight to stocks and bonds.

Commodities are publicly traded tangible assets used in commerce and trade. The most popular traded commodities are oil, gold, and base metals. Commodities are essential for growth and development. The commodity sector is vital in the economy of a developing country.
- Pre-Payments- Pre-payments are payments made in advance for the services or goods to be received later. For example, loan repayment before the due date, prepaid rent, electricity bills, salaries, tax.

Pre-Payments help a business cut down costs in the future as a well-known economic term "Inflation" affects all the expenses listed above. Therefore, it helps a business cut down its future costs in advance. They are listed under Current Assets on the balance sheet.
- Cash/trade receivables - Trade receivables, also known as accounts receivables, are the amounts to be paid to business by its users.
Trade Receivables are:
- Trade accounts receivable
- Notes receivables
- Other accounts receivables

- Inventory - Inventory serves as a major part of the business, including stocks, etc.
Inventory includes:
- Raw materials
- Component parts
- Work in progress
- Finished goods
- Packing & packaging

Inventory serves the following functions in a business:
- Provide & maintain good service to its customers
- Smooth flow of goods through the productive process
- Provide protection and assurance against uncertainty in supply or demand
- To obtain an efficient utilization of resources such as people and equipment.
- Cash Equivalents - Cash equivalents are used in the liquidity ratio calculations to determine the ability of the company to pay off its short-term debt. The main purpose of cash equivalents is for short-term investing. It possesses high credit quality and is highly liquid.
Cash equivalents are one of the three main asset classes in financial investing with stocks and bonds.

Businesses invest in cash equivalents to earn interest on their funds until the time they don't need it in their business. After that, it plays a role in the financial acquisition and is used in purchasing inventories, meeting operating expenses, and for several other purchases.
- Other Liquid Assets - Other liquid assets include certificates of deposit, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and mutual funds (they are slightly less liquid assets than stocks and ETFs).

Precious metals can also be considered valuable & liquid assets and thus can be used as currency. Money market funds are like mutual funds that only own highly liquid assets.
Key Takeaways
- From the above statements, we can conclude that all assets that can be liquified are classified as current assets. Managers use this information for the company's proper functioning and for stakeholders to help them make judgments.
- They can be found under the category of current liabilities in the statement of financial statement.
- Ratio analysis possesses the ability to understand if a business is profitable or not. It is also used to make decisions and understand where a company stands compared to its peers belonging to the same industry.
- They are short-term assets consumed within one financial year, whereas non-current assets are long-term assets that possess an economic life of more than a year.
- They include cash, cash equivalents, inventory, trade receivables, pre-payments, and other liquid assets.
Everything You Need To Master Excel Modeling
To Help You Thrive in the Most Prestigious Jobs on Wall Street.
Researched and authored by Abhinav Bhardwaj | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:


or Want to Sign up with your social account?